TL;DR: “Not your keys, not your coins” has resulted in over $100 billion lost or stolen since the early 2010s. Zengo is the leading MPC wallet that secures over 1 million customers. Check it out, or read below to learn more about MPC wallets.
The mantra of “not your keys not your crypto” is as powerful today as it was in 2017. But the result? Lost and stolen seed phrases, misplaced private keys, stress for new users, and a flight to CeFi exchanges and ‘crypto banks.’
An estimated $100 billion dollars of Bitcoin (just Bitcoin) has been lost forever, because of private key mismanagement.
As a community, crypto has been dogmatically clinging to a purported “private key gold standard,” more obsessed about the technology than providing what people actually need. MPC is a solution that already exists, recently championed by companies like Coinbase and Zengo.
Simple and secure MPC technology is already being used at the institutional level – companies like Fireblocks are helping custody billions of dollars of cryptoassets with MPC cryptography. It’s time average users get the same bulletproof security as the big players, and developers understand the security benefits of MPC to onboard more crypto users.
For years the status-quo perpetuated a dangerous misconception: There are only 2 ways to store crypto. This false dichotomy is why so many potential crypto-enthusiasts haven’t started to get involved in the ecosystem.
Custody cryptoassets in a centralized exchange, giving up your freedom, control, and on-chain access in return for relative security, simplicity, and comfort knowing someone else will worry about secure crypto storage.
Use an on-chain crypto wallet with private keys, rendering assets vulnerable to scammers, hacks, lost or misplaced keys – but knowing you have ultimate control over your crypto: to store, HODL, or lose…
There’s actually a better way: A hybrid solution in the form of a type of cryptography called MPC, or multi-party computation.
MPC stands for secure Multi-Party Computation and is a field of cryptography born 30 years ago.
Generally, MPC allows two (or more) parties to jointly compute a function output without revealing their inputs. For example: Using MPC, a group of friends can securely calculate their average salary (“output”), without revealing how much each of them gets (“inputs”).
Specifically for cryptocurrency wallets, MPC allows the creation of a secure key management system without a single point of failure (the proverbial “private key”) in which multiple parties (for example a remote server and a mobile phone) can jointly perform all needed cryptographic functions (like key generation, transaction signatures and transaction verification) while neither of the parties reveal their respective secrets. It is important to highlight that in MPC a single private key is never generated, split, or reconstructed in the process: This makes it superior to traditional models based on a single private key.
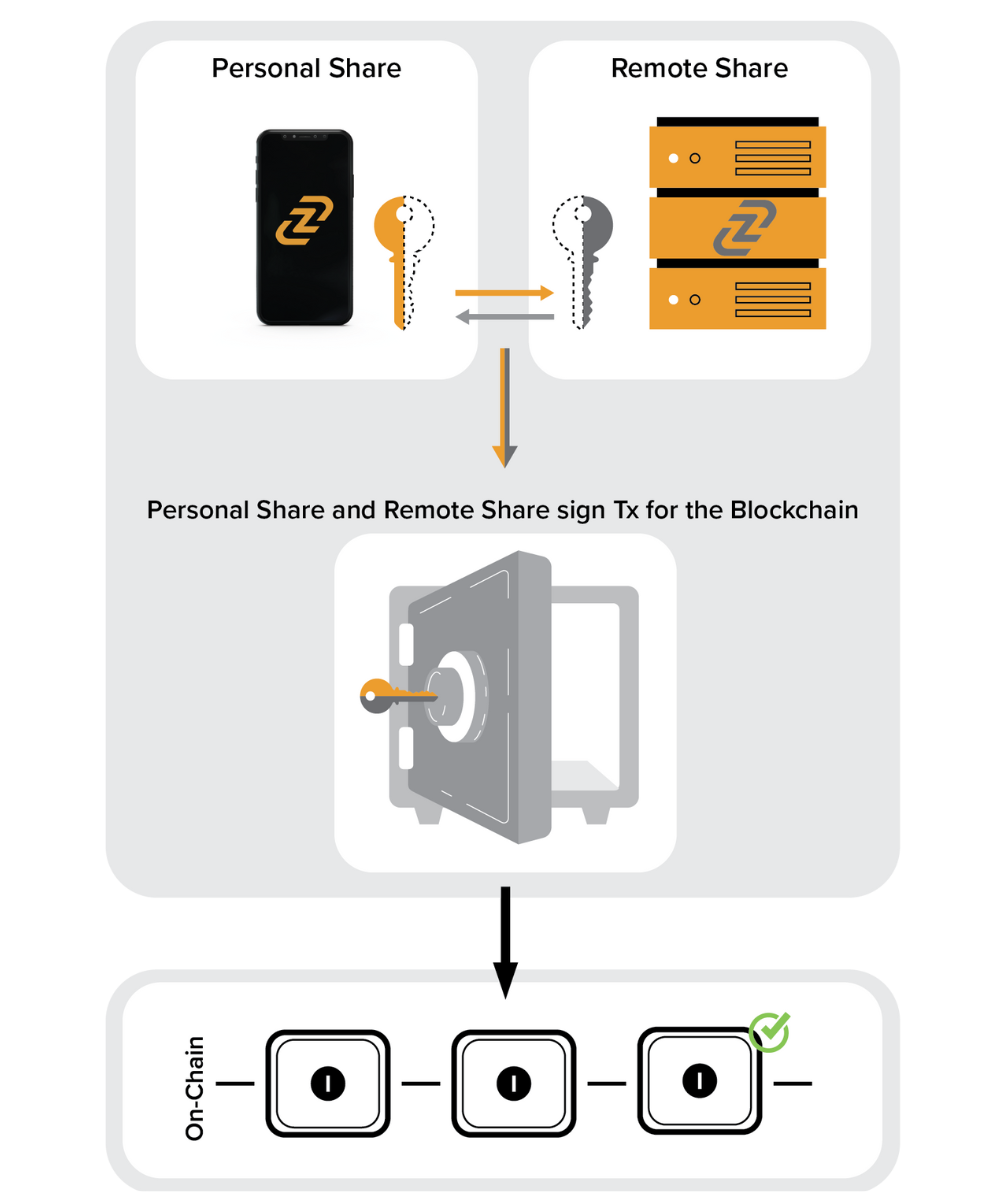
By implementing this type of MPC technology, consumer-focused wallets (and institutional services) can securely design an on-chain asset management system that removes the single point of failure of a private key. This offers a more secure self-custodial option by protecting against both private key theft (as there is no single private key to steal) and key loss, as each party can back up their secret input individually in a way that does not expose and compromise the entire system.
This design offers a number of advantages:
Learn more on the Zen Crypto Show podcast, here.
This type of recovery is immediately more familiar and far less scary for the majority of people. Almost everyone who has created an account of any kind online knows how to recover their login using an email, trusted contact, cloud backup, or their biometric scan.
This is why these types of recoverability are crucial for bringing new people into crypto systems. Implementing familiar solutions for recovery will allow more people to feel comfortable using crypto.
Once in the ecosystem, some will want different types of security or options with a low centralization risk. There is nothing preventing anyone from using multiple wallets once they have started using crypto. In fact, it is encouraged to use more than 1 wallet when storing cryptoassets.
There is, however, a HUGE barrier to entry with the majority of wallets for the majority of people: Seed phrases.
Having a single phrase that can move the entire contents of an account in an instant can be scary. Some people are willing to rely fully on themselves to keep something this important safe. Most people are not.
Having a path to enter crypto for the first time, try applications, and hold assets where users DON’T have to worry about a seed phrase is CRITICAL for the next 1 Billion people to join the world of #Web3.

MPC wallets like Zengo replace the traditional private key with two independently created mathematical “secret shares.” One share is stored on your mobile device and the other on the Zengo server.
With no single point of failure, even if something happens to one of the shares, no one can access your crypto but you.
To understand the type of cryptography behind MPC it’s helpful to learn about TSS (Threshold Cryptography) which is a subfield of MPC.
In TSS cryptography, cryptographic operations are defined with a threshold assumption in mind – it is assumed that at least a threshold of the parties involved in the computation are acting honestly and not controlled by an attacker at the same time. It could be two parties, or more. Learn more about TSS here.

While Zengo was the 1st crypto wallet to support MPC for consumers, companies like Fireblocks have been managing billions of dollars of assets for some of the world’s leading crypto institutions for years. Coinbase recently announced support for an MPC-powered Dapp browser inside of their custodial crypto wallet.
As MPC offers the optimal balance between on-chain self-custody, wallet security and crypto recoverability, it is only a matter of time until MPC becomes widely adopted.
MPC works by splitting the traditional private keys into multiple pieces, distributing them in multiple places to ensure no one person has full access to the traditional private key. The major advantage here is that the private key is always used in a distributed manner.
When a transaction signature is required, the parties involved (in Zengo there are two: the Zengo server and the user’s phone) in order to separately run a computation to make whatever you wanted to happen on the blockchain, well, happen! The best part of this process is no single entity can ever get access to any private key: There is no single point of vulnerability. Even if an attacker tried to get access to one of the two shares, they can’t access all of the ‘secret shares’ simultaneously, making your digital assets much safer than in the traditional private key architecture.
A number of billion-dollar institutions are using by MPC technology, including Fireblocks, Coinbase, and Zengo.
MPC technology is actually dozens of years old – initial development began in the 1980s – but applied MPC technology to crypto wallets is a relatively recent technological innovation in the last decade.
A major advantage of MPC, in addition to its security and recoverability benefits, includes the fact that it is chain-agnostic. Unlike multi-signature (MultiSigs) approaches which do not support every blockchain, MPC can be applied to many. Zengo actively contributes to open-source MPC material on GitHub, learn more here.
© 2024 Zengo Ltd. All rights reserved.
Enter your phone number to receive a download link.
